Success Story: Custom Solutions for Highly Corrosive Media Challenges

Analytical instruments and laboratory equipment demand precise fluid control, making them a critical application area for instrumentation valves and fittings. Additionally, analytical processes often involve hazardous materials, such as corrosive, toxic, or reactive substances. High-quality valves and fittings play a crucial role in preventing leaks and ensuring the safe handling of these materials, thereby safeguarding both personnel and the environment. Leveraging extensive expertise in product design and industry applications, FITOK provides valve and fitting solutions that meet stringent industry standards, addressing customer needs for safety, reliability, and performance.

Harsh Working Conditions
Microwave digestion is a technique that utilizes microwaves to digest samples, which includes processes such as dissolution, drying, ashing, and leaching. It is typically used for large-scale preparation of various samples. Concentrated or mixed acids are commonly used as digestion solvents because they can destroy or dissolve the matrices of organic and inorganic samples, turning the entire sample into a solution. During microwave digestion, the client needs to heat highly corrosive concentrated acids or mixed acids under certain pressures. It is crucial that the valve components in the pressure-containing apparatus are not damaged by these corrosive substances to avoid failure in gas tightness.
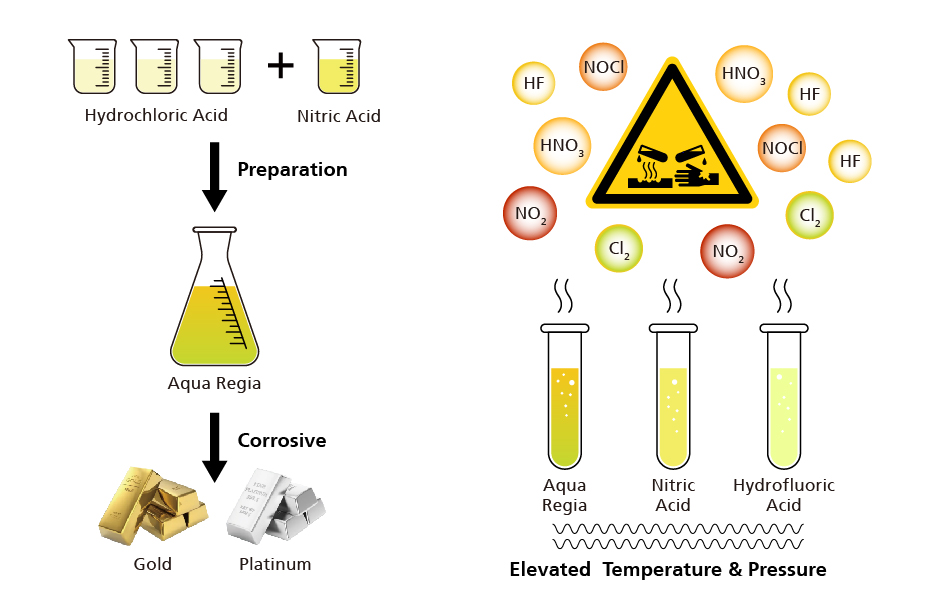
Figure 1 Aqua Regia Preparation(Left) and Microwave Digestion(Right)
One widely used digestion solvent is aqua regia, known for its strong corrosiveness and yellow fumes. It is one of the few liquids that dissolves noble metals like gold and platinum. Aqua regia can be prepared by mixing concentrated hydrochloric acid (HCl) with concentrated nitric acid (HNO₃) in a volume ratio of 3:1. It is generally employed in etching processes and some analytical detection methods. In the client's operating environment, corrosive mixed gaseous media are generated under heating conditions from aqua regia, nitric acid, and hydrofluoric acid solutions. These mixed gases include potentially produced nitric vapor, nitrogen dioxide, hydrofluoric acid, chlorine gas, and nitrous chloride, all of which are strong oxidizing acidic gases.
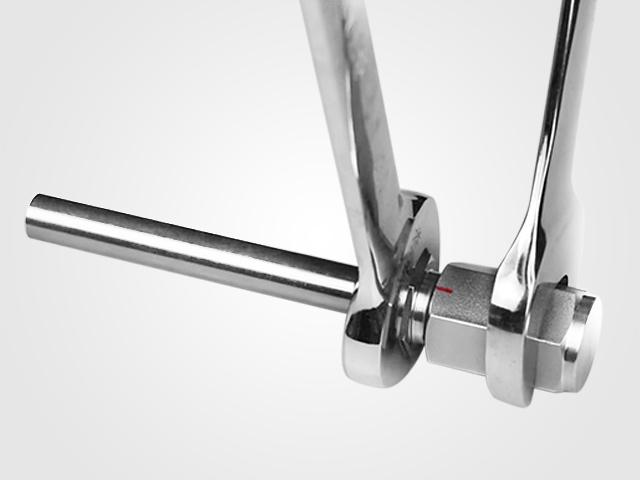
The client conducted tests using conventional valves, and when the pressure reached 160 bar with valve temperatures between 50°C and 80°C, the standard material valves quickly began to leak due to degradation from strong corrosive media. The internal springs corroded and failed, while the sealing O-rings became brittle and broke. If the corrosion resistance issue of the valve components in this environment could not be resolved, the client would face delays in product development timelines and struggle to meet product lifespan standards. Faced with this predicament, the client ultimately turned to FITOK for a solution.
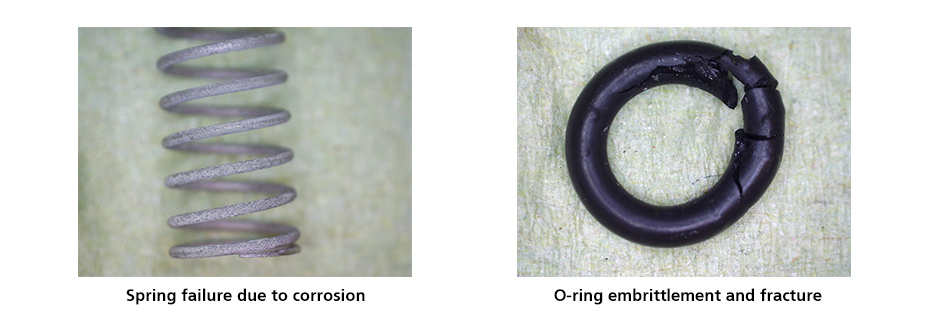
Figure 2 Failure of Conventional Valve Components
Collaborating with FITOK to Overcome Challenges
To address this challenge, FITOK customized valve bodies and internal components using Alloy 6Mo (S31254) and Alloy C-276 for this specific working condition. Additionally, to better align with the client's application requirements, the FITOK R&D team opted to replace the sealing material with PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). PTFE demonstrates superior chemical stability compared to FFKM (perfluoroelastomer) and is virtually unaffected by any corrosive substances, including strong acids, strong bases, and organic solvents, while maintaining stable performance over a wide temperature range. Although PTFE exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, its material is harder and less elastic than rubber, making its sealing performance more susceptible to contaminants. Thus, achieving a reliable seal with PTFE became the most significant challenge in the structural design process.

Figure 3 CV Series Check Valves of Alloy C-276 and PTFE Seal Component
Since the original structure used to secure rubber O-rings cannot effectively hold PTFE sealing components, the FITOK team redesigned the corresponding structure to ensure sealing performance. Additionally, considering that the sealing performance of PTFE is susceptible to contamination, the poppet structure was optimized to maximize the sealing capabilities of the valve. Ultimately, with the excellent corrosion resistance of Alloy C-276 and PTFE, as well as the professional structural design by FITOK's technical team, the valve's technical indicators—including corrosion resistance, sealing performance, and lifespan—were significantly improved.
In the latest design iteration, extensive testing and lifespan evaluations have confirmed that the final product meets strict quality standards even in harsh corrosive environments, leading to successful delivery. This also resolves customer issues regarding delays in development progress and challenges with product lifespan not meeting standards.
In this collaboration, the client utilized a range of FITOK products, including 6D Series tube fittings, CV Series check valves, FW Series filters, high-pressure needle valves, and quick-connects. The FITOK team actively engaged with the client to address various issues during testing and provided timely solutions, earning the client's trust. FITOK's professional technical team is capable of tackling even the most challenging fluid medium environments. By leveraging our extensive experience in corrosion-resistant material design, we accomplish tasks that other manufacturers cannot.
If you would like to learn more about how to collaborate with FITOK and implement customized solutions for your fluid system challenges, please leave a message online, and we will get back to you as soon as possible!
Related Articles:







.jpg)
.jpg)
 Back
Back 

